GNU Scientific Library (GSL) - The GNU Scientific Library 2.x. - Messages
#1 Posted: 8/27/2013 5:53:11 PM
GNU Scientific Library (GSL)







Functions list:
Solvers for Non-Stiff Systems:
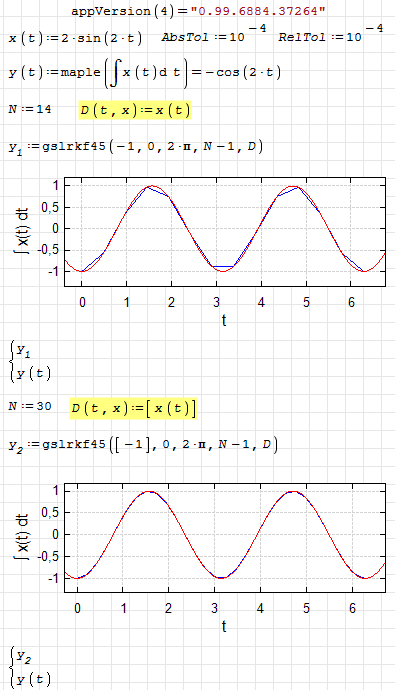
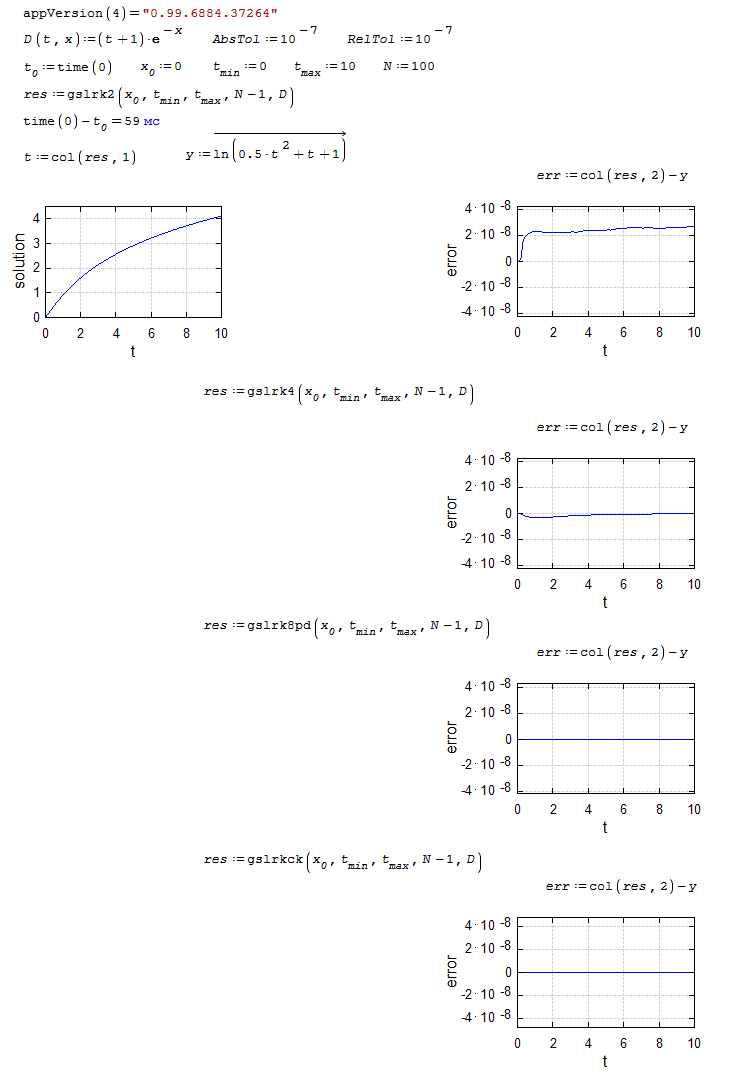
gslrk2(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2, 3) method.
gslrk4(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrkf45(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg (4, 5) method.
gslrkck(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4, 5) method.
gslrk8pd(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8, 9) method.
Arguments:
- init is either a vector of n real initial values, where n is the number of unknowns (or a single scalar initial value, in the case of a single ODE).
- x1 and x2 are real, scalar endpoints of the interval over which the solution to the ODE(s) is evaluated. Initial values in init are the values of the ODE function(s) evaluated at x1.
- intvls is the integer number of discretization intervals used to interpolate the solution function. The number of solution points is the number of intervals + 1.
- D is a vector function of the form D(x,y) specifying the right-hand side of the system
Options:
- AbsTol - absolute tolerance parameter, default value 1E-7.
- RelTol - relative tolerance parameter, default value 1E-4.
Examples:
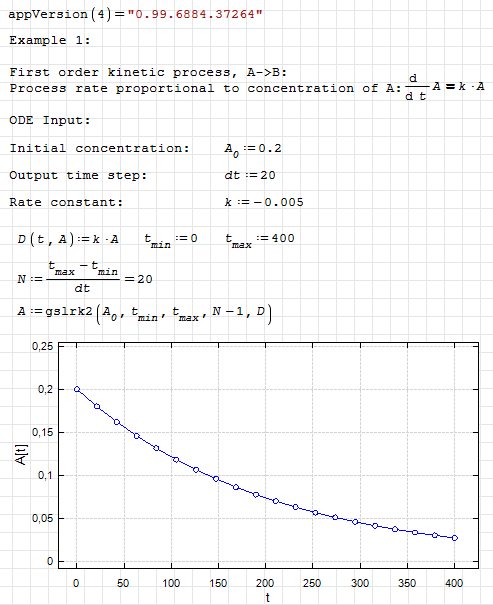
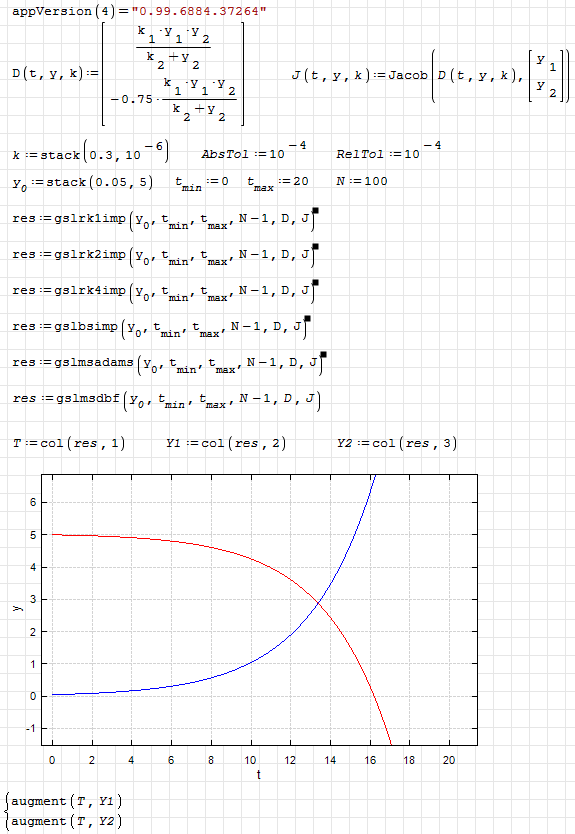
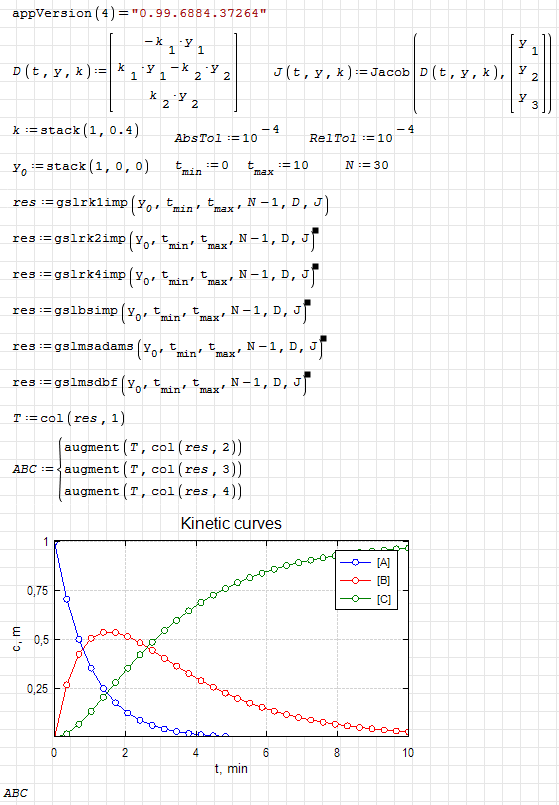
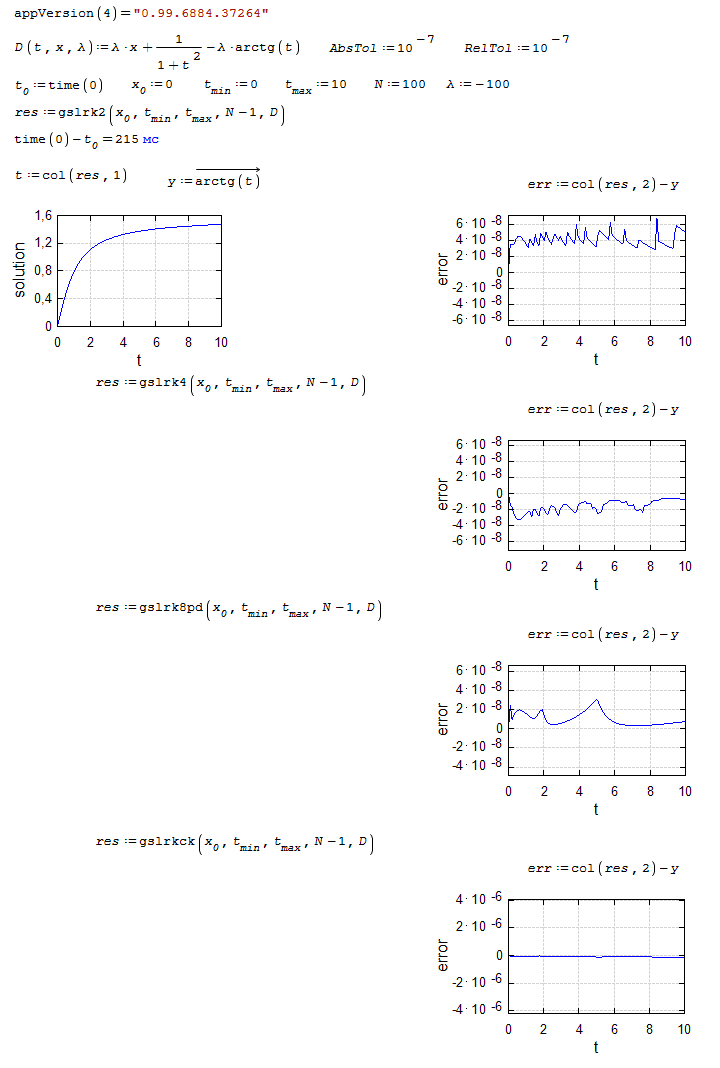
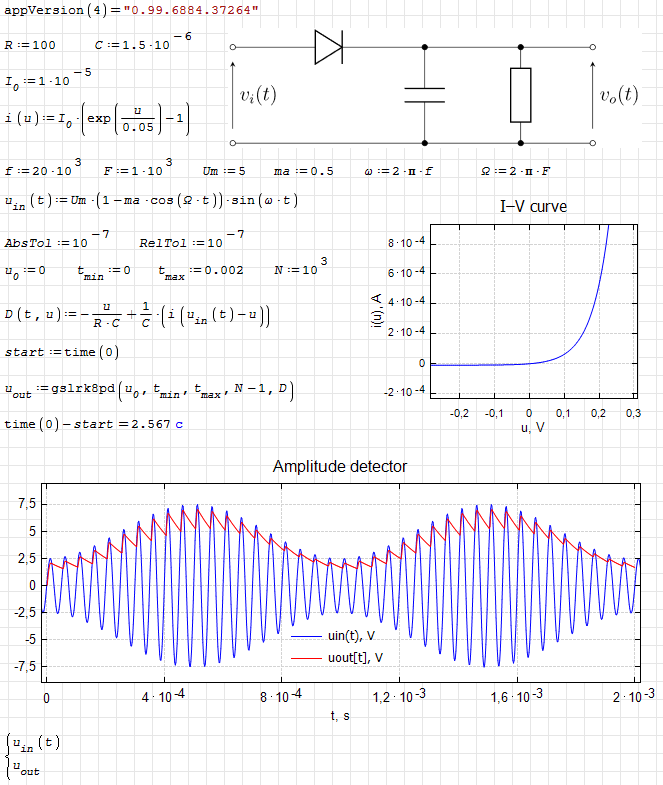
gsl.ode.integrate.sm (11.45 KiB) downloaded 1282 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.sm (8.27 KiB) downloaded 1293 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.sm (14.94 KiB) downloaded 1306 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.sm (14.73 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.sm (19.22 KiB) downloaded 1284 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.sm (18.87 KiB) downloaded 1269 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.sm (20.19 KiB) downloaded 1340 time(s).
gsl.ode.integrate.pdf (92.44 KiB) downloaded 662 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.pdf (77.32 KiB) downloaded 633 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.pdf (92.67 KiB) downloaded 599 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.pdf (91.09 KiB) downloaded 588 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.pdf (110.61 KiB) downloaded 575 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.pdf (110.4 KiB) downloaded 625 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.pdf (148.63 KiB) downloaded 617 time(s).
Links:
1. GNU Scientific Library – Reference Manual.
2. GSL for Windows.
3. The GSL Team.
4. Thanks.
See also:
● [topic=726]Mathcad Toolbox[/topic]
● [topic=1918]DotNumerics[/topic]
● [topic=13809]SADEL[/topic]
● [topic=1970]Matlab C++ Math Library[/topic]
● [topic=17063]OSLO[/topic]
● [topic=17067]lsoda[/topic]
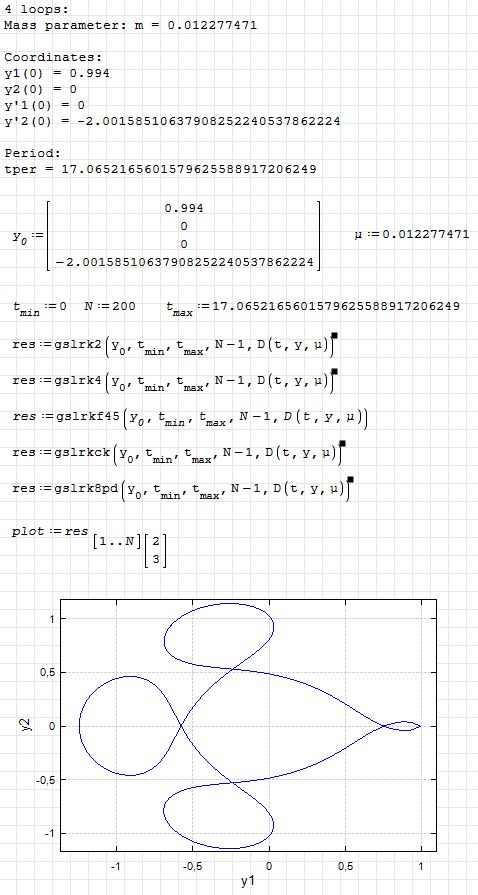
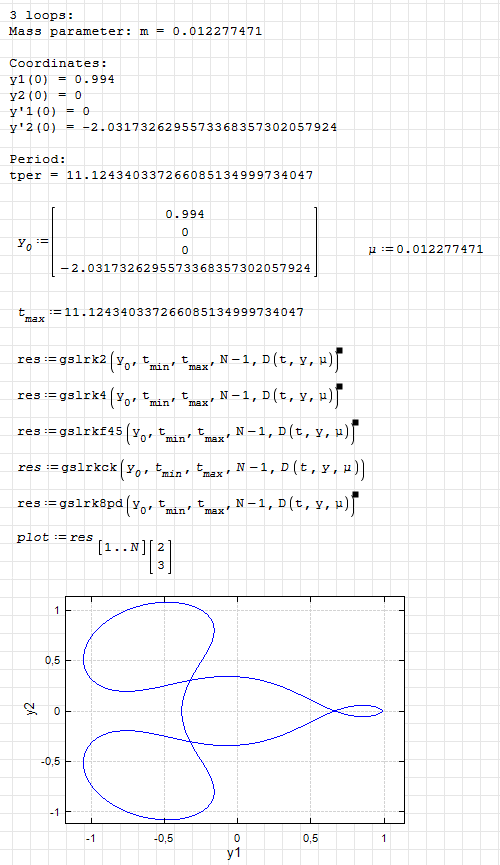
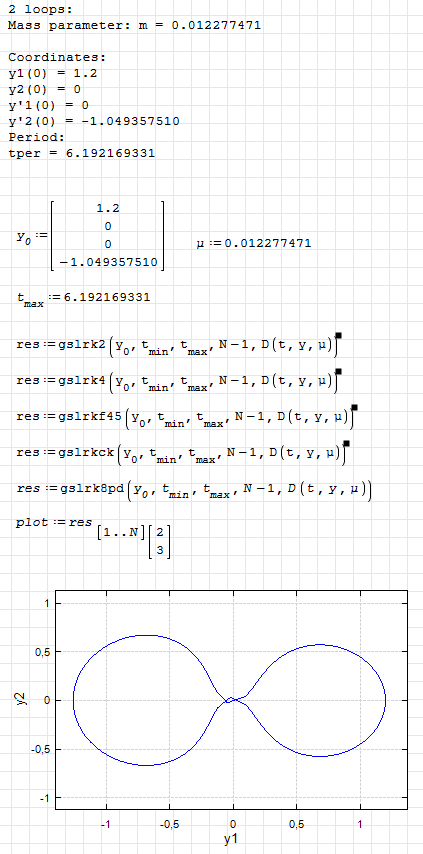
GNU Scientific Library. ODE Solvers. Arenstorf orbit.pdf (99.51 KiB) downloaded 958 time(s).







Functions list:
gslbsimp(1) - (cmd) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslmsadams(1) - (cmd) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(1) - (cmd) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslrk1imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk2(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4(1) - (cmd) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk8pd(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrkck(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gsl_deriv_backward(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive backward difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_deriv_central(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive central difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_deriv_forward(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive forward difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_sf_airy(1) - (cmd) compute the Airy function.
gsl_sf_airy(2) - (flags,x) compute the Airy function.
gsl_sf_bessel(1) - (cmd) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_bessel(2) - (flags,x) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_bessel(3) - (flags,n|nu|l,x) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_clausen(1) - (x) calculate the Clausen integral.
gsl_sf_dawson(1) - (x) calculate the Dawson integral.
gsl_sf_debye(2) - (n,x) calculate the Debye function.
gsl_sf_dilog(1) - (x) calculate the Dilogarithm.
gsl_sf_ellint_D(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral D(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Dcomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral D(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_E(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral E(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Ecomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral E(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_F(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral F(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Kcomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral K(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_P(3) - (ϕ,k,n) compute the incomplete elliptic integral P(ϕ,k,n).
gsl_sf_ellint_Pcomp(2) - (k,n) compute the complete elliptic integral Π(k,n).
gsl_sf_ellint_RC(2) - (x,y) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RC(x,y).
gsl_sf_ellint_RD(3) - (x,y,z) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RD(x,y,z).
gsl_sf_ellint_RF(3) - (x,y,z) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RF(x,y,z).
gsl_sf_ellint_RJ(4) - (x,y,z,p) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RJ(x,y,z,p).
gsl_sf_eta(1) - (s) calculate the eta function η(s) for arbitrary s.
gsl_sf_eta_int(1) - (n) calculate the eta function η(n) for integer n.
gsl_sf_hzeta(2) - (s,q) calculate the Hurwitz zeta function ζ(s,q) for s > 1, q > 0.
gsl_sf_zeta(1) - (s) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(s) for arbitrary s ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zetam1(1) - (s) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(s) minus one for arbitrary s ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zetam1_int(1) - (n) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(n) minus one for integer n ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zeta_int(1) - (n) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(n) for integer n ≠ 1.
gsl_version - returns GSL version.
gslbsimp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslbsimp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Bulirsch-Stoer method of Bader and Deuflhard.
gslmsadams(1) - (cmd) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsadams(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep Adams method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(1) - (cmd) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslmsdbf(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) variable-coefficient linear multistep backward differentiation formula (BDF) method in Nordsieck form.
gslrk1imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk1imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian first order Runge-Kutta (implicit Euler or backward Euler) method.
gslrk2(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2,3) method.
gslrk2imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk2imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4(1) - (cmd) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrk4imp(1) - (cmd) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk4imp(6) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y),J(x,y)) implicit Gaussian second order Runge-Kutta (implicit mid-point) method.
gslrk8pd(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrk8pd(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8,9) method.
gslrkck(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkck(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(1) - (cmd) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(3) - (ode,y(x),xmax) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(4) - (ode,y(x),xmax,steps) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gslrkf45(5) - (ics,xmin,xmax,steps,D(x,y)) explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4,5) method.
gsl_deriv_backward(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive backward difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_deriv_central(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive central difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_deriv_forward(3) - (f,x,h) computes the numerical derivative of the function f at the point x using an adaptive forward difference algorithm with a step-size of h.
gsl_sf_airy(1) - (cmd) compute the Airy function.
gsl_sf_airy(2) - (flags,x) compute the Airy function.
gsl_sf_bessel(1) - (cmd) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_bessel(2) - (flags,x) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_bessel(3) - (flags,n|nu|l,x) compute the Bessel function.
gsl_sf_clausen(1) - (x) calculate the Clausen integral.
gsl_sf_dawson(1) - (x) calculate the Dawson integral.
gsl_sf_debye(2) - (n,x) calculate the Debye function.
gsl_sf_dilog(1) - (x) calculate the Dilogarithm.
gsl_sf_ellint_D(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral D(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Dcomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral D(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_E(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral E(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Ecomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral E(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_F(2) - (ϕ,k) compute the incomplete elliptic integral F(ϕ,k).
gsl_sf_ellint_Kcomp(1) - (k) compute the complete elliptic integral K(k).
gsl_sf_ellint_P(3) - (ϕ,k,n) compute the incomplete elliptic integral P(ϕ,k,n).
gsl_sf_ellint_Pcomp(2) - (k,n) compute the complete elliptic integral Π(k,n).
gsl_sf_ellint_RC(2) - (x,y) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RC(x,y).
gsl_sf_ellint_RD(3) - (x,y,z) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RD(x,y,z).
gsl_sf_ellint_RF(3) - (x,y,z) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RF(x,y,z).
gsl_sf_ellint_RJ(4) - (x,y,z,p) compute the incomplete elliptic integral RJ(x,y,z,p).
gsl_sf_eta(1) - (s) calculate the eta function η(s) for arbitrary s.
gsl_sf_eta_int(1) - (n) calculate the eta function η(n) for integer n.
gsl_sf_hzeta(2) - (s,q) calculate the Hurwitz zeta function ζ(s,q) for s > 1, q > 0.
gsl_sf_zeta(1) - (s) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(s) for arbitrary s ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zetam1(1) - (s) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(s) minus one for arbitrary s ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zetam1_int(1) - (n) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(n) minus one for integer n ≠ 1.
gsl_sf_zeta_int(1) - (n) calculate the Riemann zeta function ζ(n) for integer n ≠ 1.
gsl_version - returns GSL version.
Solvers for Non-Stiff Systems:
gslrk2(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta (2, 3) method.
gslrk4(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit 4th order (classical) Runge-Kutta. Error estimation is carried out by the step doubling method.
gslrkf45(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg (4, 5) method.
gslrkck(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Cash-Karp (4, 5) method.
gslrk8pd(init, x1, x2, intvls, D) Explicit embedded Runge-Kutta Prince-Dormand (8, 9) method.
Arguments:
- init is either a vector of n real initial values, where n is the number of unknowns (or a single scalar initial value, in the case of a single ODE).
- x1 and x2 are real, scalar endpoints of the interval over which the solution to the ODE(s) is evaluated. Initial values in init are the values of the ODE function(s) evaluated at x1.
- intvls is the integer number of discretization intervals used to interpolate the solution function. The number of solution points is the number of intervals + 1.
- D is a vector function of the form D(x,y) specifying the right-hand side of the system
Options:
- AbsTol - absolute tolerance parameter, default value 1E-7.
- RelTol - relative tolerance parameter, default value 1E-4.
Examples:










gsl.ode.integrate.sm (11.45 KiB) downloaded 1282 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.sm (8.27 KiB) downloaded 1293 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.sm (14.94 KiB) downloaded 1306 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.sm (14.73 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.sm (19.22 KiB) downloaded 1284 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.sm (18.87 KiB) downloaded 1269 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.sm (20.19 KiB) downloaded 1340 time(s).
gsl.ode.integrate.pdf (92.44 KiB) downloaded 662 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.pdf (77.32 KiB) downloaded 633 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.pdf (92.67 KiB) downloaded 599 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.pdf (91.09 KiB) downloaded 588 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.pdf (110.61 KiB) downloaded 575 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.pdf (110.4 KiB) downloaded 625 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.pdf (148.63 KiB) downloaded 617 time(s).
Links:
1. GNU Scientific Library – Reference Manual.
2. GSL for Windows.
3. The GSL Team.
4. Thanks.
See also:
● [topic=726]Mathcad Toolbox[/topic]
● [topic=1918]DotNumerics[/topic]
● [topic=13809]SADEL[/topic]
● [topic=1970]Matlab C++ Math Library[/topic]
● [topic=17063]OSLO[/topic]
● [topic=17067]lsoda[/topic]
GNU Scientific Library. ODE Solvers. Arenstorf orbit.pdf (99.51 KiB) downloaded 958 time(s).
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
4 users liked this post
Martin Kraska 8/28/2013 3:21:00 AM, Radovan Omorjan 8/28/2013 12:54:00 AM, ioan92 8/28/2013 2:54:00 AM, Davide Carpi 8/27/2013 6:21:00 PM
#2 Posted: 8/27/2013 6:21:50 PM
very very cool library, there are several interesting things 
works for me (win 7 x64)
best regards,
Davide
works for me (win 7 x64)
best regards,
Davide
If you like my plugins please consider to support the program buying a license; for personal contributions to me: paypal.me/dcprojects
#3 Posted: 8/28/2013 1:18:41 AM
I agree with Davide. I mentioned this library few times as well 
As I said before, uni is like a man working in a candy store and giving us very good and healthy sweets for free

Regards,
Radovan
As I said before, uni is like a man working in a candy store and giving us very good and healthy sweets for free
Regards,
Radovan
When Sisyphus climbed to the top of a hill, they said: "Wrong boulder!"
2 users liked this post
#4 Posted: 8/28/2013 3:27:27 AM
Uni,
I see you do not use prefixes any more. Does that mean, you are considering the GSL as the primary source of generic SMath functions? IMHO that would be sensible, as GSL seems to be the most vital and most free library among the ones you wrapped so far. However, I have no idea about performance issues.
I see you do not use prefixes any more. Does that mean, you are considering the GSL as the primary source of generic SMath functions? IMHO that would be sensible, as GSL seems to be the most vital and most free library among the ones you wrapped so far. However, I have no idea about performance issues.
Technische Mechanik mit SMath Studio: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-658-50592-9
1 users liked this post
Davide Carpi 8/28/2013 3:58:00 AM
#5 Posted: 8/28/2013 3:33:37 AM
Functions that are not yet implemented not have a prefix. When I add a function in the plug-in, I add a prefix to it. All the functions in this library will have the same or similar names which given in their description.
For example: gsl_sf_bessel_J0() -> gslsfJ0(), gsl_sf_airy_Ai() -> gslsfAi(), ...
I'll ask Andrey to implement the namespace for functions. This option may be enabled and disabled as the description of the region. In this case, you can specify the function names without the prefix.
For example: gsl_sf_bessel_J0() -> gslsfJ0(), gsl_sf_airy_Ai() -> gslsfAi(), ...
I'll ask Andrey to implement the namespace for functions. This option may be enabled and disabled as the description of the region. In this case, you can specify the function names without the prefix.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
1 users liked this post
Davide Carpi 8/28/2013 3:58:00 AM
#6 Posted: 8/28/2013 4:50:52 AM
WroteI'll ask Andrey to implement the namespace for functions. This option may be enabled and disabled as the description of the region. In this case, you can specify the function names without the prefix.
I am not sure that I understand correctly, what the namespace for functions concept is meant to be.
Is that something like local aliasing?
Is that a by-region setting?
What is the visualization concept?
I'd expect something like switching on aliasing (and perhaps enabling of the plugin) by a separate statement "with("GLS" ) or with("Matlab" ). This could be
deactivated later in the same sheet by a function without() in a traceable manner.
BTW, how about including a plugin hint in the description string of the functions. I had to search the forum in order to find out what plugin provides the erf() function (Davide, sorry for my leaking memory). Not a big deal for me, but would help to correctly direct user feedback.
Technische Mechanik mit SMath Studio: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-658-50592-9
#7 Posted: 8/28/2013 5:13:24 AM
WroteI'd expect something like switching on aliasing (and perhaps enabling of the plugin) by a separate statement "with("GLS" ) or with("Matlab" ). This could be
deactivated later in the same sheet by a function without() in a traceable manner.
I think it only works for the document in text form. It is unlikely that this method will be useful in our case.
We have one example of namespace support. Not necessarily indicate the selected space, but the user should be able to select it. We can assign a hot key to display the namespace for the selected function.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
1 users liked this post
Davide Carpi 8/28/2013 1:39:00 PM
#8 Posted: 8/28/2013 5:51:42 AM
Wrote
As I said before, uni is like a man working in a candy store and giving us very good and healthy sweets for free
I see viacheslav and davide more like fabulous dwarves blacksmiths and radovan and martin like mere mortal betatesters, thanks btw :d
#9 Posted: 8/28/2013 8:04:36 AM
Ok, it is a Mathcad concept (I was not aware of that).
The example with m as units and m as variable does not really convince me. By math standards, these items should be distinguished by type face (italic for variables, upright for units or other items that are not supposed to change. SMath has this the other way around, but at least clearly indicates the difference. Thus, the unit name space tag is the apostrophe ' in front of the name.
There is another "namespace" then in SMath, the absolute variables with ~ as tag (which would be fine to represent matrix/vector values).
An option for getting along without new features would be to leave the prefixes in the names and to provide generic names pointing to the most appropriate function from whatever plugin it may come or even to provide wrapper functions like Findroot() to choose from what is available.
The ordinary ("mortal" ) user hardly wants to choose from 20 ode solvers or from 10 nonlinear solvers.
The example with m as units and m as variable does not really convince me. By math standards, these items should be distinguished by type face (italic for variables, upright for units or other items that are not supposed to change. SMath has this the other way around, but at least clearly indicates the difference. Thus, the unit name space tag is the apostrophe ' in front of the name.
There is another "namespace" then in SMath, the absolute variables with ~ as tag (which would be fine to represent matrix/vector values).
An option for getting along without new features would be to leave the prefixes in the names and to provide generic names pointing to the most appropriate function from whatever plugin it may come or even to provide wrapper functions like Findroot() to choose from what is available.
The ordinary ("mortal" ) user hardly wants to choose from 20 ode solvers or from 10 nonlinear solvers.
Technische Mechanik mit SMath Studio: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-658-50592-9
#10 Posted: 8/28/2013 11:21:27 AM
Updated to GSL 1.16.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
3 users liked this post
Davide Carpi 8/28/2013 1:39:00 PM, Radovan Omorjan 8/28/2013 4:42:00 PM, ioan92 8/29/2013 8:51:00 AM
#11 Posted: 9/16/2016 10:37:36 AM
Updated for the fully automatic build using Release Manager.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
#12 Posted: 6/23/2018 5:49:08 PM
Installing this plugin causing forced close on Arch Linux + Mono.
After forced close you cannot be able to open Smath again unless manually deleting the plugin.
Regards
After forced close you cannot be able to open Smath again unless manually deleting the plugin.
Regards
#13 Posted: 6/23/2018 6:36:27 PM
Because the plugin is not compatible with Linux + Mono:
Win32 + x64 - means Windows only, C++/CLI - unmanaged code used.
QuoteVS2013, .Net 2.0, C#, C++/CLI, Win32 + x64
Win32 + x64 - means Windows only, C++/CLI - unmanaged code used.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
#14 Posted: 8/1/2018 12:19:18 PM
gslrkck simple test.
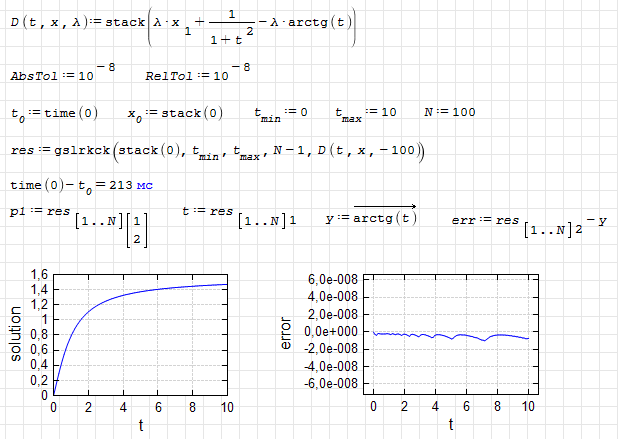
gslrkck.test1.sm (11.34 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gslrkck.test1.pdf (48.07 KiB) downloaded 571 time(s).

gslrkck.test1.sm (11.34 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gslrkck.test1.pdf (48.07 KiB) downloaded 571 time(s).
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
1 users liked this post
sergio 8/1/2018 6:07:00 PM
#15 Posted: 12/12/2018 8:12:57 AM
Updated.
Changes:
- zero point issue fixed;
- added support for the simple D(t,x) definition.
Changes:
- zero point issue fixed;
- added support for the simple D(t,x) definition.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
4 users liked this post
Andrey Ivashov 12/12/2018 9:34:00 AM, Radovan Omorjan 12/12/2018 9:07:00 AM, sergio 12/12/2018 9:16:00 AM, frapuano 12/12/2018 9:33:00 AM
#16 Posted: 12/24/2018 12:50:43 PM
Updated.






gsl.ode.kinetic1.sm (8.27 KiB) downloaded 1293 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.sm (14.94 KiB) downloaded 1306 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.sm (14.73 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.sm (19.22 KiB) downloaded 1284 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.sm (18.87 KiB) downloaded 1269 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.sm (20.19 KiB) downloaded 1340 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.pdf (77.32 KiB) downloaded 633 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.pdf (92.67 KiB) downloaded 599 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.pdf (91.09 KiB) downloaded 588 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.pdf (110.61 KiB) downloaded 575 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.pdf (110.4 KiB) downloaded 625 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.pdf (148.63 KiB) downloaded 617 time(s).






gsl.ode.kinetic1.sm (8.27 KiB) downloaded 1293 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.sm (14.94 KiB) downloaded 1306 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.sm (14.73 KiB) downloaded 1274 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.sm (19.22 KiB) downloaded 1284 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.sm (18.87 KiB) downloaded 1269 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.sm (20.19 KiB) downloaded 1340 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic1.pdf (77.32 KiB) downloaded 633 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic2.pdf (92.67 KiB) downloaded 599 time(s).
gsl.ode.kinetic3.pdf (91.09 KiB) downloaded 588 time(s).
gsl.ode.test1.pdf (110.61 KiB) downloaded 575 time(s).
gsl.ode.test2.pdf (110.4 KiB) downloaded 625 time(s).
gsl.ode.Amplitude detector.pdf (148.63 KiB) downloaded 617 time(s).
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
4 users liked this post
sergio 12/24/2018 1:23:00 PM, frapuano 12/24/2018 2:23:00 PM, Radovan Omorjan 12/24/2018 2:53:00 PM, Alvaro 12/25/2018 1:33:00 AM
#17 Posted: 1/21/2019 9:23:03 PM
Updated.
Added: gslmsadams(5), gslrk1imp(5), gslrk2imp(5), gslrk4imp(5), gslbsimp(5), gslmsbdf(5).
Fixed: gslrk1imp(6), gslrk2imp(6), gslrk4imp(6), gslbsimp(6), gslmsbdf(6).
Removed: gslmsadams(6).
Solvers with 5 arguments working with numerical Jacobian (not so good but I don't know how to improve it now).


Added: gslmsadams(5), gslrk1imp(5), gslrk2imp(5), gslrk4imp(5), gslbsimp(5), gslmsbdf(5).
Fixed: gslrk1imp(6), gslrk2imp(6), gslrk4imp(6), gslbsimp(6), gslmsbdf(6).
Removed: gslmsadams(6).
Solvers with 5 arguments working with numerical Jacobian (not so good but I don't know how to improve it now).
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
3 users liked this post
frapuano 1/22/2019 5:02:00 AM, Radovan Omorjan 1/22/2019 5:32:00 AM, Davide Carpi 1/22/2019 7:43:00 AM
#18 Posted: 5/14/2019 10:33:45 AM
I was on a journey.
This use of the library is beyond the scope of the forum. I will try to create a simple example, but you still need to read the original documentation to use the library.
This use of the library is beyond the scope of the forum. I will try to create a simple example, but you still need to read the original documentation to use the library.
Russia ☭ forever, Viacheslav N. Mezentsev
- New Posts
- No New Posts

